It's all cloud could and cloud now-a-days. Everyone are moving towards the cloud for making life easier.
In this post I will be explaining on how to extract/Import data from SharePoint Lists which is hosted on SharePoint Online of Office 365 using SSIS.
There is no direct way to connect to the SharePoint Online using SSIS.
For connecting to SharePoint Online using SSIS, we need the below components installed before stating.
In this post I will be explaining on how to extract/Import data from SharePoint Lists which is hosted on SharePoint Online of Office 365 using SSIS.
There is no direct way to connect to the SharePoint Online using SSIS.
For connecting to SharePoint Online using SSIS, we need the below components installed before stating.
- Microsoft OData Source for Microsoft SQL Server 2012
Download from http://www.microsoft.com/en-in/download/details.aspx?id=42280 - SharePoint Server 2013 Client Components SDK
Download from http://www.microsoft.com/en-in/download/details.aspx?id=35585
Once you download and Install both the components,
- Open the Visual Studio and create a new Integration Services Package
- Drag and Drop "Data Flow Task"
- In the "Data Flow Task" Drag and Drop "OData Source"
- Right-Click on "OData Source" and Click Edit
- Enter the "Connection Manager Name" and "Service Document Location" For Service Document Location, append "/_vti_bin/listdata.svc" to the SharePoint site
For Office 365, we need to use "User this user name and password" - Click "All" and change the "Microsoft Online Services Authentication" to True
- Click "Test Connection"
- Click "OK"
- Then Choose "Collection" in "User Collection or resource path"
- In the "Collection" choose the list you want to import
- When you click on "Preview..." you will be able to see the data from the list
- Now add the destination connection and run the package to import data from the SharePoint Online list













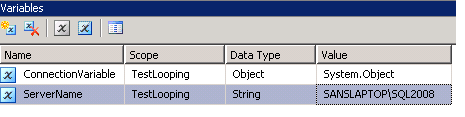







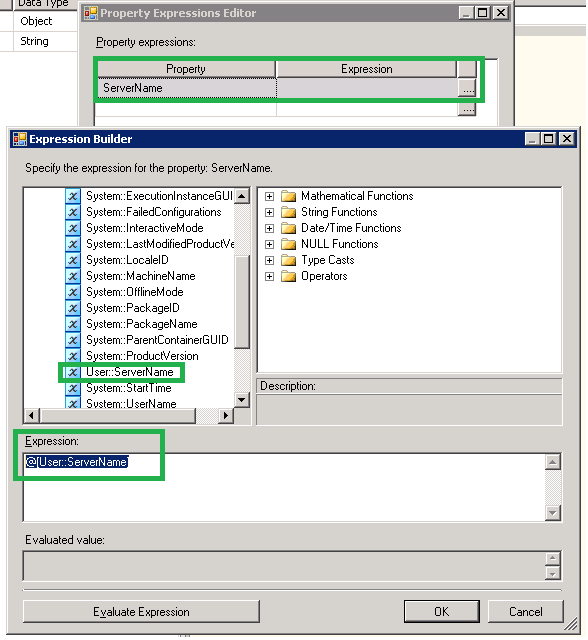
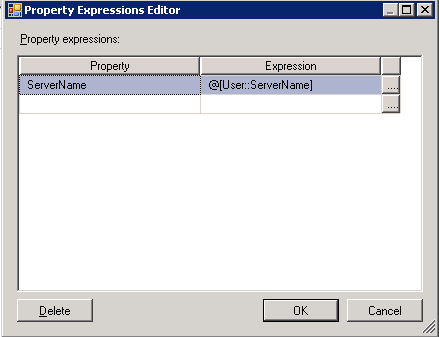

 3. Click OK
3. Click OK  5. Now go back to the Connections tab and type in the file path of the Excel 2007 file along with the file name there.
5. Now go back to the Connections tab and type in the file path of the Excel 2007 file along with the file name there. 