SELECT session_id AS SPID, command AS [Command], a.text AS Query, start_time AS [Start Time], percent_complete AS [Percent Complete], dateadd(second,estimated_completion_time/1000, getdate()) AS [Estimated Completion Time] FROM sys.dm_exec_requests r CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(r.sql_handle) a WHERE r.command like 'BACKUP%' OR r.command like 'RESTORE%')
Friday, May 20, 2022
T-SQL to find Backup or Restore Progress
Here is a script that comes handy while performing a huge database Backup or Restore. This script provides the details on the progress of the Backup or Restore operation including the estimated finish time.
Sunday, March 12, 2017
T-SQL script to get Backup Details of a Database and the Sequence it was taken
Here is an handy script which give the details of the list of backup(s) taken of a database and the sequence it was taken.
DECLARE @db_name VARCHAR(100) SELECT @db_name = '<DB Name>' SELECT BS.server_name AS [Server Name] ,BS.database_name AS [Database Name] ,BS.recovery_model AS [Recovery Model] ,BMF.physical_device_name [Location] ,(CAST(BS.backup_size / 1000000 AS INT)) AS [Size of Backup (MB)] ,CASE BS.[type] WHEN 'D' THEN 'Full' WHEN 'I' THEN 'Differential' WHEN 'L' THEN 'Transaction Log' END AS [Type of Backup] ,BS.backup_start_date AS [Backup Date] ,BS.first_lsn AS [First LSN] ,BS.last_lsn AS [Last LSN] FROM msdb.dbo.backupset BS INNER JOIN msdb.dbo.backupmediafamily BMF ON BS.media_set_id = BMF.media_set_id WHERE BS.database_name = @db_name ORDER BY backup_start_date DESC , backup_finish_date
Download the script from https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/T-SQL-script-to-get-Backup-5a9b029b?redir=0
Labels:
Backup,
Backup Location,
Differential Backup,
Full Backup,
Log Backups,
LSN,
Sequence,
T-SQL
Wednesday, October 5, 2016
SQL Backup Recovery Tool to Repair Damaged SQL Backup - Product Review - A guest Post by Daniel Jones
It has been commonly observed that many users are inclined to store the important and crucial data in SQL Server due to its reliable and consistent data storage feature. All the data is stored efficiently in data files i.e. MDF and NDF files. Unfavourable situations like server breakdown, system corruption etc can arise at any moment. The smart users prefer to take the backup of desired database, which can be restored during unexpected conditions. Many cases have been reported where the users are completely hopeless as their backup files (.bak) got damaged or corrupted due to reasons like virus attack or malware etc. No provision is provided by the server or operating system to recover data from such backup files. However, various third party tools promise to repair damaged SQL backup files without any data loss. One such well-known automated tool is SQL Backup Recovery Tool, which empowers to repair full database from corrupted/damaged backup file. Our data recovery experts have undergone through the software and tested it under the following environment:

Dual File Scan Mode
The tool has been designed to offer scanning of damaged backup files in the following two modes:


Preview Repaired SQL Data
Once the complete backup file is scanned, the tool provides preview of all repaired database components. The user can choose to preview all database component like tables, views, triggers, columns, functions, keys etc.


Multiple Export Options
The users are offered to export the repaired data in any of the following way:

Export Schema Options
SQL backup recovery tool provides two export modes for the users. Depending on requirement, the user can choose to export data as:

- Operating System- Windows 8
- Mounted RAM- 2 GB
- Processor Used-2.5 GHz
The testing has been done in such a way that all of its features can be evaluated to determine the SQL backup recovery tool on the basis of quality, reliability, performance, security etc. The following section is focused to provide a transparent review of the tool on the basis of expert’s experience.
Functional Features of SQL Backup Recovery Tool
While working with the recovery tool in different working environments, the experts encountered several amazing features which differentiates it from other tools available in industry. Some of the major features, which makes the tool excel in recovery field are mentioned below:
Complete Backup File Recovery
The tool facilitates the recovery of all MDF and NDF files from the corrupted backup file i.e., various database components such as tables, views, functions, triggers, keys, indexes get recovered from the chosen backup file.

Dual File Scan Mode
The tool has been designed to offer scanning of damaged backup files in the following two modes:
- Quick Scan - This mode scans the backup file with minimum corruption
- Advance Scan - This mode scans the backup file with major corruption issues (highly damaged files)

Multiple Backup File Recovery
SQL backup recovery tool provides Multiple Backup File Options to let the user add multiple backup files or folder for data recovery. So if user faces an issue where multiple backup files got corrupted, this multiple backup option can be chosen to recover all data.
SQL backup recovery tool provides Multiple Backup File Options to let the user add multiple backup files or folder for data recovery. So if user faces an issue where multiple backup files got corrupted, this multiple backup option can be chosen to recover all data.

Preview Repaired SQL Data
Once the complete backup file is scanned, the tool provides preview of all repaired database components. The user can choose to preview all database component like tables, views, triggers, columns, functions, keys etc.

Batch export Recovered Data
The tool allows the user to export selected database components from the scanned data. The user can make selective choice to transport the required database objects from the backup file.
The tool allows the user to export selected database components from the scanned data. The user can make selective choice to transport the required database objects from the backup file.

Multiple Export Options
The users are offered to export the repaired data in any of the following way:
- Export To SQL Server Database - It allows to export selected repaired data directly into SQL Server by providing database credentials.
- Export as SQL Server Compatible Script - It generates SQL script, which is compatible for any SQL Server version.

Export Schema Options
SQL backup recovery tool provides two export modes for the users. Depending on requirement, the user can choose to export data as:
- With only schema - It allows to export only with database schema for the backup file
- With schema & data - It allows to extract both data and schema for the backup file

Primary/Foreign Key Recovery
Along with the data recovery, the tool also helps to recover both primary and foreign keys of all the tables. So, we can say that the tool ensures to maintain data integrity of the data recovered from the backup file.
Perks of The Tool
In addition to above discussed features, the tool offers some additional features like auto-detection of SQL Server, no database size restriction, interactive user interface etc.
Specifications of SQL Backup Recovery Tool
The tool has been designed to work efficiently under the following hardware and software specifications:
Along with the data recovery, the tool also helps to recover both primary and foreign keys of all the tables. So, we can say that the tool ensures to maintain data integrity of the data recovered from the backup file.
Perks of The Tool
In addition to above discussed features, the tool offers some additional features like auto-detection of SQL Server, no database size restriction, interactive user interface etc.
Specifications of SQL Backup Recovery Tool
The tool has been designed to work efficiently under the following hardware and software specifications:
- Operating System - It supports Windows 8.1 & all below versions
- Processor Requirement - Minimum 1 GHz is mandatory for tool installation. The experts suggest to use 2.4 GHz processor for faster processing.
- Mounted RAM - 512MB should be allocated at minimum. For larger storage, 1 GB can be used depending on requirement.
- SQL Server - It repair damaged SQL backup file of SQL Server 2014 & all the below versions
Available Versions of SQL Backup Recovery Tool
The tool to repair damaged SQL backup file can be availed in two versions:
- Demo Version - Users can download the free version from company’s official website. It offers scan and preview of the backup files.
- Licensed Version - The paid version of the tool can be purchased from company’s website. It allows to scan, preview and export the selected backup file
PROS
- The tool provides recovery of backup files even without SQL Server installation on the system.
- The tool offers the recovery of highly corrupted backup files using advance scan.
CONS
- The generated scanned files cannot be saved on the local system, which creates need for rescanning in future use.
Conclusion
After working on various aspects of the software, we can conclude that SQL Backup Recovery tool fulfils all the expectations to repair damaged SQL backup file. The users can go for this tool for an efficient bak file recovery within few easy steps. The tool can be rated as 9.8 on the scale of 10 as it provides an excellent approach to repair the corrupted or damaged backup files using its interactive user interface.
About Daniel Jones
Daniel Jones is a SQL Server DBA and contributor at SQL Tech Tips. Having 2 + years of experience in SQL recovery and system infrastructure.
Social Media Profiles
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/danieljones05
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/daniel-jones-5bb87a115
Social Media Profiles
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/danieljones05
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/daniel-jones-5bb87a115
Labels:
Backup,
Backup Recovery,
Guest Post,
MSSQL,
Product Review
Thursday, May 21, 2015
Restore database from corrupt SQL database backup file - Another Guest Post by Jyoti Prakash
Often people have corruption issues regarding
Microsoft's SQL server database as well as its backup. Basically, backup is the
only way to make your database secured and protective; it helps you to restore
your inaccessible files of the main database when any type of corruption or
damage occurs. But, what if backup also corrupt, while attempting to restore
database from backup file. There could be multiple reasons behind such disaster
situation, here in this write-up you will get to know about the reason and
solutions behind such case, where SQL Server user faces corruption in SQL
Server database backup and not able to restore their databases.
How and why the backup file gets corrupt:
SQL backup files are basically a replica of your
original SQL database, which can be located in different locations on the
system. There could be multiple reasons of inaccessible backup file. Here are
some most common causes of damaged SQL BAK files:
- Virus attack
- Abrupt system shutdown
- Use of a wrong driver
- Bad sectors in your system's hard disk
- Sudden removal of a selected tables,
records, and procedures
- unconventional functioning of Hard disk
- Improper shutdown of application
- Wrong database synchronization
- System crash
- corrupt database system rules and tables
The most common error message during restoration of
database is: 'Backup or restore
operation terminating abnormally.'
A Backup restoration error occurs when a filemark in
the backup device could not be read. There could be multiple causes of when a
user encounters a filemark error. The most common reasons are:
- A media failure may arise on the same device where the backup is stored
- A write failure may occur while creating the backup file
- Loss of connectivity may arise while creating a network backup
- A failure in the Input/Output path occurs in the disk just after successful write to the disk
Manual Solution:
After backup restore error the first thing you could
do is to check whether all the sets of backup have issues or just some sets
have issues. It might be possible that only some sets of backup have issues due
to which you are getting restore error. In order to retrieve other backup sets
from the device, you need to specify the file number. In case, there are
multiple backup sets available on a single device, then to determine the usable
backup, you can run the following query:
RESTORE HEADERONLY
FROM DISK='<Backup Location>'
If you got the usable set from the disk, copy it to another drive for
usage and try to restore the damaged files with the help of SQL restore
commands. Here are some of the SQL commands that you can use to restore
corruption in your SQL database backup.
To recover
a database use the following command. This will put your database in the
"restoring" state
RESTORE DATABASE
<DB Name> FROM DISK='<Backup Location>' WITH FILE = <FileNumber>
Note: Write the backup set number instead of 'FileNumber'
that you want to restore.
The following command will take the database, which is in 'restoring'
state and make it available for end users.
RESTORE LOG
<DB Name> FROM DISK = '<Backup Location>'
WITH RECOVERY
WITH RECOVERY
The above mentioned commands are used to restore
corrupt backup file of SQL database. However, these corrupt backup recovery
solutions provided by Microsoft are not applicable for deep corruption cases.
In order to restore your highly damaged or corrupt SQL backup database you can
always choose a third party SQL backup recovery software. These professional
utilities are designed to restore data from a corrupt (.BAK) SQL backup
file.
Third party applications have functions to restore SQL
backup file due to all above mentioned reasons. Before buying any professional
backup recovery tool, you need to choose the most reliable one. For that you
should use the online demo versions of the backup recovery applications to test
their efficiency.
About Jyoti Prakash
Jyoti is a Sr. DBA - SQL Server at Stellar Data Recovery and has written several article on SQL Server disaster recovery planning & fixing. In addition, she spend her time on Technical forums helping people with the issues related to SQL server.
Labels:
Backup,
Backup and Restore,
Guest Post
Monday, May 26, 2014
T-SQL to find backup location
Here is a T-SQL query to find the location of the backup files.
SELECT database_name AS DBName
,physical_device_name AS BackupLocation
,CASE WHEN [TYPE]='D' THEN 'FULL'
WHEN [TYPE]='I' THEN 'DIFFERENTIAL'
WHEN [TYPE]='L' THEN 'LOG'
WHEN [TYPE]='F' THEN 'FILE / FILEGROUP'
WHEN [TYPE]='G' THEN 'DIFFERENTIAL FILE'
WHEN [TYPE]='P' THEN 'PARTIAL'
WHEN [TYPE]='Q' THEN 'DIFFERENTIAL PARTIAL'
END AS BackupType
,backup_finish_date AS BackupFinishDate
FROM msdb.dbo.backupset JOIN msdb.dbo.backupmediafamily
ON(backupset.media_set_id=backupmediafamily.media_set_id)
ORDER BY backup_finish_date DESC
Labels:
Backup,
Backup Location
Sunday, December 8, 2013
Size of a Backup is more than the Database
Recently one of my Junior DBA came up with a question to me relating to the size of the Backups.
The question was, How will the size of the backup be more than the database size?

We all know that the size of the backup will be less than or equal to the size of the database and no chance of increasing.
So what could be wrong in this case?
The question was, How will the size of the backup be more than the database size?

So what could be wrong in this case?
Labels:
Backup
Thursday, September 26, 2013
Split backups in SQL Server
Split backup is a method of performing the backups on a SQL Server database to multiple files.
When we perform the split backups on a database, the SQL server engine creates multiple backup files with the size split into the number of files mentioned in the backup command.
When we perform the split backups on a database, the SQL server engine creates multiple backup files with the size split into the number of files mentioned in the backup command.
BACKUP DATABASE [SansSQL] TO DISK = N'D:\Backup\SansSQL_Part1_Backup.bak' ,DISK = N'D:\Backup\SansSQL_Part2_Backup.bak' WITH INIT, STATS = 10 GO
When you execute backup command like above then the backup of that particular database will be split into 2 different files of almost equal size.
This can be used with Full, Differential and Log backups as well.

Labels:
Backup,
Split Backup
Wednesday, May 1, 2013
LSN mismatch error in Log Shipping
LSN mismatch is a common issue which happens in Log Shipping and because of which the Log Shipping goes out of sync.
When you check the history, you will find messages like below
When you check the history, you will find messages like below
| Msg 4305, Level 16, State 1, Line 1 The log in this backup set begins at LSN 36000000048400001, which is too recent to apply to the database. An earlier log backup that includes LSN 20000000022100001 can be restored. Msg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Line 1 RESTORE LOG is terminating abnormally. |
Labels:
Backup,
Log Backups,
Log Shipping,
LSN
Saturday, January 5, 2013
Password Protect a backup file
Password protection of databases backups helps a lot in protecting the database backup from misuse.
Once such case is, when you are sending a backup of database physically through disks which has very sensitive and critical data to a different office or data center.
To password protect backup file, you have include WITH PASSWORD option when backing up the database
Answer: The restoration will fail with the below error
Once such case is, when you are sending a backup of database physically through disks which has very sensitive and critical data to a different office or data center.
To password protect backup file, you have include WITH PASSWORD option when backing up the database
-- Full Backup with password BACKUP DATABASE SansSQL TO DISK = 'D:\Backup\SansSQL_FullBackup.bak' WITH PASSWORD = 'Password123'Now, once the backup is taken with a password, the same password has to be provided while restoring for matching the decryption sequence.
--Restore Full backup with no recovery RESTORE DATABASE SansSQL FROM DISK = 'D:\Backup\SansSQL_FullBackup.bak' WITH RECOVERY, PASSWORD='Password123'Question 1: What happens if you give a wrong password or try to restore without giving password?
Answer: The restoration will fail with the below error
| Msg 3279, Level 16, State 2, Line 1 Access is denied due to a password failure Msg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Line 1 RESTORE DATABASE is terminating abnormally. |
Question 2: How will you come to know if a backup is password protected?
Answer: When you try to restore, it will give an error saying "Access is denied due to a password failure"
And when you try to execute RESTORE HEADERONLY, the file name will be shown as "*** PASSWORD PROTECTED ***"

Wednesday, October 31, 2012
Backup job failed - "file manipulation operations"
On some occasions when scheduling maintenance jobs like, Full database backup, Shrink database, Differential backups, index maintenance jobs we oversee the schedules and end up with jobs running into each other.
This will definitely lead to bigger errors and failures at any point in time. One such error we come across in such situations is the following.
"Backup, file manipulation operations (such as ALTER DATABASE ADD FILE) and encryption changes on a database must be serialized. Reissue the statement after the current backup or file manipulation operation is completed."
Note: This is just the part of job history.
Fixes:
- All we need to do is be alert and make sure we have the correct schedules for all the jobs without allowing any of the jobs running into each other.
- If error or failures, make sure to change the job schedules and confirm if it works fine.
Hope this helps!
Tuesday, September 11, 2012
Database Corruption and Recovery
What is database corruption?





Inconsistency in the internal structure of the database with
respect to data or log files is known as database corruption
What causes database Corruption?
- Physical Inconsistency - One or more access paths to the data may be invalid.
- Logical Inconsistency - One or more pointers to the data may be invalid
How to detect Corruption?
- Status of database set to “suspect”
- Evident from Error log and/or Event Viewer logs
- Consistency errors from DBCC CHECKDB
- T-SQL Queries or application throwing corruption related error (Database might be online without being suspect)
- SQL Server Startup Failure
- Failure while Restoring or Attaching databases
What are the causes that leads to database corruption?
- Hardware failure event
- Power outage
- SAN crash
- NTFS or File System Corruption
- FTDisk Errors
- Bad Block or Disk Corruption
- Outdated or Faulty Drivers
- Failed Restore/Attach
- Due to Bad File/Page
- Abnormal Termination of the process
- Corrupted Header
- User Error
- File Deletion/Renaming
- File Swapping
- 3rd Party Software
- Filter Drivers
- Outdated/Faulty Device Driver
Recovery Flows
- master Database

- model Database

- msdb Database

- tempdb Database

- User Database

Labels:
Backup,
Backup and Restore,
Database Corruption,
Recovery
Tuesday, September 27, 2011
Backup Database to multiple locations simultaneously - Mirror Backups
Database backup is one the regular activity a DBA would perform. Some times you might come across a situation where in you need to backup the database to different location. When I say backup database to different locations, it means that a copy of backup file needs to be placed on a different location as well and this is different from the Split Backups.


This is can be achieved by different methods,
- Take backup and then copy to multiple location
- Take backup of the same database multiple times pointing to different locations
- Use "MIRROR TO" Option in the Backup command
Using the option "MIRROR TO" is very simple, you just need to mention "MIRROR TO" and "WITH FORMAT" options in the normal BACKUP DATABASE Statement and you are done. The backup database statement with these two options will take the backup of the same database to multiple locations at the same time.
This option "MIRROR TO" is introduced in SQL Server 2005 and this works only in SQL Server 2005 Enterprise Edition and later versions.
This can be used for all backup types and the Maximum number of "MIRROR TO" clauses that you can specify is three.
Example:
| BACKUP DATABASE AdventureWorks
TO DISK = 'C:\Backup\AdventureWorks_Full.bak'
MIRROR TO DISK = 'C:\Mirror\AdventureWorks_Full.bak'
WITH STATS=10, FORMAT
BACKUP DATABASE AdventureWorks
TO DISK = 'C:\Backup\AdventureWorks_Differential.bak'
MIRROR TO DISK = 'C:\Mirror\AdventureWorks_Differential.bak'
WITH STATS=10, DIFFERENTIAL, FORMAT
BACKUP LOG AdventureWorks
TO DISK = 'C:\Backup\AdventureWorks_log.trn'
MIRROR TO DISK = 'C:\Mirror\AdventureWorks_log.trn'
WITH STATS=10, FORMAT
|


When it comes to restoring the database, we can use either of the backup copies to restore or recover the database.
Friday, September 2, 2011
Get last backup details of all databases in a server
This stored procedure give you the information about latest backups happened on all databases in a server.
This SP works for SQL server 2005 and up.
Results:

This SP works for SQL server 2005 and up.
| Create Proc sp_BackupDetails
AS
DECLARE @BackupDetails table
([Server Name] nvarchar(500),
[Database Name] nvarchar(500),
[Last Full Backup] nvarchar(500),
[Last Differential Backup] nvarchar(500),
[Last Log Backup] nvarchar(500),
[Last File or filegroup Backup] nvarchar(500),
[Last Differential file Backup] nvarchar(500),
[Last Partial Backup] nvarchar(500),
[Last Differential Partial Backup] nvarchar(500)
)
DECLARE @DBName nvarchar(500)
Declare DBName Cursor for
Select name from sys.databases
Open DBName
Fetch Next from DBName into @DBName
While @@fetch_status = 0
BEGIN
Insert into @BackupDetails
select @@ServerName as [Server Name]
,SDB.name AS [Database Name]
,(select COALESCE(Convert(nvarchar(20), MAX(backup_finish_date), 100),'NA') from msdb..backupset where database_name=@DBName and type='D') AS [Last Full Backup]
,(Select COALESCE(Convert(nvarchar(20), MAX(backup_finish_date), 100),'NA') from msdb..backupset where database_name=@DBName and type='I') AS [Last Differential Backup]
,(Select COALESCE(Convert(nvarchar(20), MAX(backup_finish_date), 100),'NA') from msdb..backupset where database_name=@DBName and type='L') AS [Last Log Backup]
,(Select COALESCE(Convert(nvarchar(20), MAX(backup_finish_date), 100),'NA') from msdb..backupset where database_name=@DBName and type='F') AS [Last File or filegroup Backup]
,(Select COALESCE(Convert(nvarchar(20), MAX(backup_finish_date), 100),'NA') from msdb..backupset where database_name=@DBName and type='G') AS [Last Differential file Backup]
,(Select COALESCE(Convert(nvarchar(20), MAX(backup_finish_date), 100),'NA') from msdb..backupset where database_name=@DBName and type='P') AS [Last Partial Backup]
,(Select COALESCE(Convert(nvarchar(20), MAX(backup_finish_date), 100),'NA') from msdb..backupset where database_name=@DBName and type='Q') AS [Last Differential Partial Backup]
from sys.databases SDB
where SDB.name =@DBName
Fetch Next from DBName into @DBName
END
Close DBName
DEALLOCATE DBName
Select * from @BackupDetails
GO
|
Usage:
Exec sp_BackupDetails
go

Saturday, March 26, 2011
Page Level Restoration
Sometimes you might come across a situation where a particular Page of a SQL Server database gets corrupted due to various reasons. In such cases only that corrupted page can be recovered using a backup.
To explain how to recover a page from the backup, I will first need to corrupt a page on a database.
By using the below method I am going to simulate the page corruption and then recover using the backup taken before corruption.
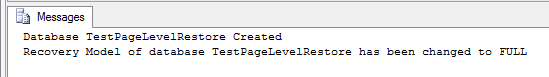
First I am going to create a database by name "TestPageLevelRestore" and Set its recovery Model to FULL.
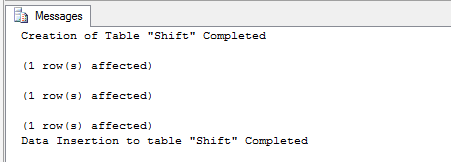
Now Create a table and insert data into that table.
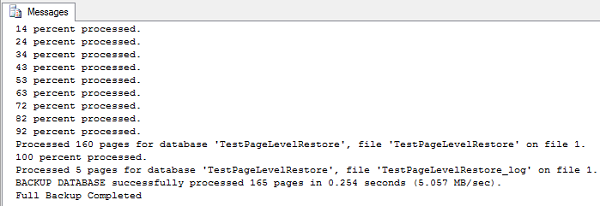
Now take a FULL backup of the database
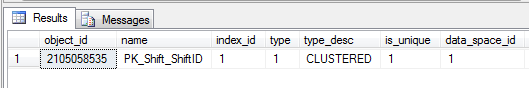
After the backup is completed, get the list of index ID's from which you can choose one to corrupt
Now get the list of pages in that index.
Now you can get the page level details using the below query
To explain how to recover a page from the backup, I will first need to corrupt a page on a database.
By using the below method I am going to simulate the page corruption and then recover using the backup taken before corruption.
First I am going to create a database by name "TestPageLevelRestore" and Set its recovery Model to FULL.
| USE master; GO CREATE DATABASE TestPageLevelRestore ON ( NAME = TestPageLevelRestore, FILENAME = 'D:\TestPageLevelRestore.mdf', SIZE = 10) LOG ON ( NAME = TestPageLevelRestore_log, FILENAME = 'D:\TestPageLevelRestore_log.ldf', SIZE = 5MB) ; GO Print 'Database TestPageLevelRestore Created' ALTER DATABASE TestPageLevelRestore SET RECOVERY FULL Print 'Recovery Model of database TestPageLevelRestore has been changed to FULL' |

Now Create a table and insert data into that table.
| Use TestPageLevelRestore GO CREATE TABLE [Shift]( [ShiftID] tinyint IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL, [Name] nvarchar(50) NOT NULL, [StartTime] datetime NOT NULL, [EndTime] datetime NOT NULL, [ModifiedDate] datetime NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT [PK_Shift_ShiftID] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED ([ShiftID] ASC) ) Print 'Creation of Table "Shift" Completed' SET IDENTITY_INSERT [Shift] ON INSERT [Shift] ([ShiftID], [Name], [StartTime], [EndTime], [ModifiedDate]) VALUES (1, N'Day', '1900-01-01 07:00:00.000', '1900-01-01 15:00:00.000', '1998-06-01 00:00:00.000') INSERT [Shift] ([ShiftID], [Name], [StartTime], [EndTime], [ModifiedDate]) VALUES (2, N'Evening', '1900-01-01 15:00:00.000', '1900-01-01 23:00:00.000', '1998-06-01 00:00:00.000') INSERT [Shift] ([ShiftID], [Name], [StartTime], [EndTime], [ModifiedDate]) VALUES (3, N'Night', '1900-01-01 23:00:00.000', '1900-01-01 07:00:00.000', '1998-06-01 00:00:00.000') SET IDENTITY_INSERT [Shift] OFF Print 'Data Insertion to table "Shift" Completed' |

Now take a FULL backup of the database
| BACKUP DATABASE TestPageLevelRestore TO DISK='D:\TestPageLevelRestore_FullBackup.bak' WITH STATS=10 Print 'Full Backup Completed' |

After the backup is completed, get the list of index ID's from which you can choose one to corrupt
| --To get the list of index ID's from which you can choose one to corrupt Use TestPageLevelRestore Select * from sys.indexes where OBJECT_NAME(object_id)='Shift' |

Now get the list of pages in that index.
| --To get the list of pages DBCC IND ('TestPageLevelRestore', 'Shift',1) |
Now you can get the page level details using the below query
| -- To display the contents DBCC TRACEON (3604); GO --TO get the page level data details DBCC PAGE('TestPageLevelRestore',1,147,3); |

For corrupting a particular page using a hex editor, you need to get the offset value, to obtain the offset value of a page simply multiply the PageID with 8192
| --Get the Offset Value. This can be obtained by multiplying the page ID with 8192. --Once you get the result copy the result and set the database to offline SELECT 147*8192 AS [OffSetValue] |

Once you get the offset Value, just copy it and take the database Offline.
| USE MASTER ALTER DATABASE TestPageLevelRestore SET OFFLINE Print 'Database TestPageLevelRestore is set to Offline. Now Open the TestPageLevelRestore.mdf file in the hex editor and press ctrl+g to go the page where the index data is located. Choose Decimal and paste the offset value. once you go to the location, then manuplate the value and save the file and exit hex editor. After manuplating data bring database online.' |

Now Open the data file of the database "TestPageLevelRestore.mdf" file in the hex editor and press ctrl+g to go the page where the index data is located.
Then choose Decimal option and paste the offset value.
Once you go to the location, then manuplate the value and save the file and exit hex editor.


You can now see that I have edited the page and saved the file.

Once you edit the file and saved it, exit the Hex Editor and bring back the database to Online state.
| USE MASTER ALTER DATABASE TestPageLevelRestore SET ONLINE Print 'Database TestPageLevelRestore is set to Online' |

Now try to read data from the table and you will get error which states that the read failed at page (x:xxxx)
| --Select the data and you will get error stating that the read failed at page (x:xxxx) USE TestPageLevelRestore Select * from shift select * from sys.master_files where DB_NAME(database_id)='TestPageLevelRestore' |

So this means that the page is now corrupted. By this the simulation of page corruption is completed.
Now we need to start looking on how to recover the page using page level restore.
Before we start the recovery process, we need to backup the tail of the log.
| USE master BACKUP LOG TestPageLevelRestore TO DISK = 'D:\TestPageLevelRestore_log.bak' WITH INIT, NORECOVERY; GO |
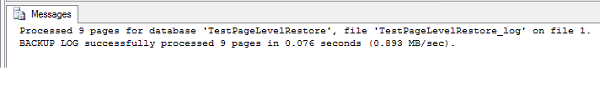
| Restore DATABASE TestPageLevelRestore Page='1:147' FROM DISK='D:\TestPageLevelRestore_FullBackup.bak' |

After the page restoration is completed, Restore the tail log backup.
| RESTORE LOG TestPageLevelRestore FROM DISK = 'D:\TestPageLevelRestore_log.bak'; GO |
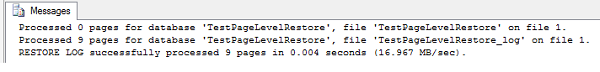
Now you have restored the corrupted page from a good backup and this can be verified by selecting the data from the table and you will be able to retrieve the data.
| USE TestPageLevelRestore Select * from shift |

The complete demo script that I have used in this post can be downloaded from here.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)

