In today's data-driven world, businesses rely on various technologies to manage, analyse, and leverage their data effectively. Three key components in this data ecosystem are databases, data warehouses, and data lakes. Each serves a unique purpose and offers specific advantages. In this blog post, we'll explore the differences between these three data storage and management solutions, provide examples of when to use each, and highlight some popular tools for implementing them.
What is a Database?
Databases are structured, organized systems designed for efficient data storage and retrieval. They are typically used to support transactional applications and are optimized for read and write operations. Databases are ideal for managing structured data, such as customer information, inventory, and financial records.
Scenario:
Suppose you run an e-commerce website, and you need to store customer data, order details, and product inventory. In this case, you would use a relational database like MSSQL, MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle to ensure data integrity and consistent transactions.
Common Database Tools:
- MSSQL: A proprietary relational database management system developed by Microsoft.
- MySQL: A popular open-source relational database management system.
- PostgreSQL: Known for its extensibility and support for complex data types.
- Oracle Database: A robust commercial database management system.
What is a Data Warehouse?
A data warehouse is designed for analytical processing and reporting. It acts as a central repository that stores data from various sources, making it easier to analyse and gain insights from historical data. Data warehouses are structured to support complex queries and reporting tools.
Scenario:
Imagine you are a retail company that wants to analyse sales data, track inventory trends, and gain insights into customer behaviour. You would consolidate data from your e-commerce platform, inventory systems, and customer relationship management (CRM) tools into a data warehouse. This allows you to run complex SQL queries and generate reports using tools like Tableau or Power BI.
Common Data Warehouse Tools:
- Snowflake: A cloud-based data warehousing platform known for its scalability.
- Amazon Redshift: A managed data warehouse service by AWS.
- Google BigQuery: Google Cloud's serverless data warehouse for fast, SQL-like querying.
What is a Data Lake?
A data lake is a repository that stores vast amounts of raw data, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Data lakes are suitable for storing diverse data types, such as logs, images, videos, and more. Unlike data warehouses, data lakes allow for the storage of data without a predefined structure.
Scenario:
Suppose you're a tech company handling a massive amount of data, including user-generated content, logs, and sensor data. Storing all this information in a data lake (e.g., Amazon S3 or Azure Data Lake Storage) provides you with the flexibility to structure and analyse the data when necessary. You can use tools like Apache Spark or Hadoop to process and derive insights from the raw data.
Common Data Lake Tools:
- Amazon S3: Amazon Web Services object storage service often used as a data lake.
- Azure Data Lake Storage: Microsoft Azure's data lake storage solution.
- Hadoop: An open-source framework for distributed storage and processing of large datasets.
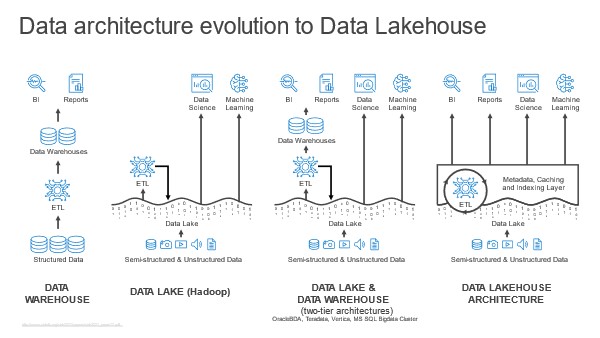
What is a Data Lakehouse?
The data lakehouse is a relatively new concept that combines the best of data lakes and data warehouses. It aims to provide the flexibility of a data lake for storing diverse, raw data while adding structured query capabilities typically associated with data warehouses. This hybrid approach often uses technologies like Delta Lake, which adds ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) transactions and schema enforcement to the data lake.
Scenario:
Consider a healthcare organization that needs to store a massive volume of patient data, including electronic health records, medical images, and diagnostic data. Using a data lakehouse with Delta Lake, they can ingest and store raw data from various sources and, at the same time, enforce data integrity, run complex queries, and generate reports for research and patient care.
Common Data Lakehouse Tools:
- Delta Lake: An open-source storage layer that brings ACID transactions to data lakes.
- Databricks: A unified analytics platform that supports Delta Lake for building data lakehouses.
- AWS Glue: Amazon's data integration and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) service for data lakehouse architecture.
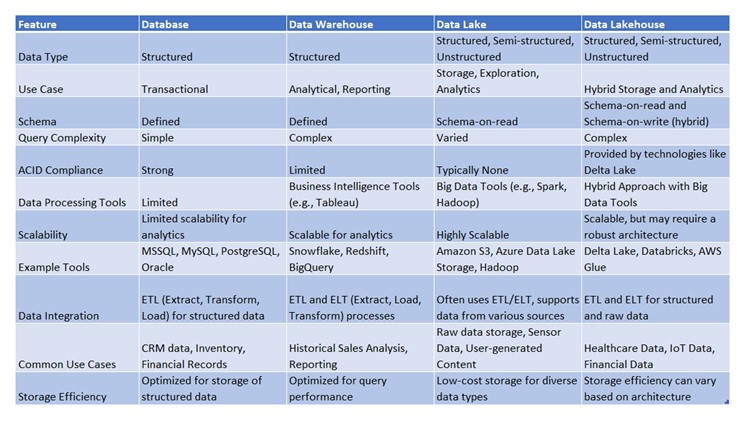
Comparison Summary
Choosing the Right Solution
The choice between a database, data warehouse, data lake, or data lakehouse depends on the specific business needs and the nature of the data. Here's a quick summary to help you decide:
- Use a database for structured data, transactional operations, and maintaining data integrity.
- Opt for a data warehouse when you need to consolidate, analyse, and report on historical data for decision-making.
- Employ a data lake when dealing with diverse, raw data types and want flexibility in structuring and processing.
- Consider a data lakehouse when you need both flexibility and structured query capabilities, combining the best of data lakes and data warehouses.
In practice, many organizations use a combination of these solutions to meet their data storage and analysis requirements. By understanding the differences between databases, data warehouses, data lakes, and data lakehouses, you can make informed decisions and harness the full power of your data while embracing modern data management techniques.

